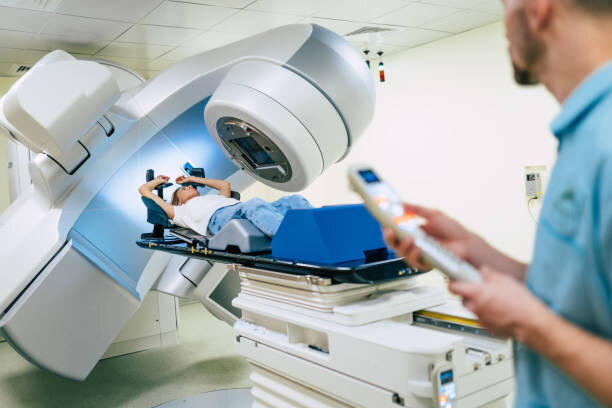
When we talk about cancer treatment, we often hear about surgery and chemotherapy, but another crucial component is radiation therapy. In fact, approximately 50% of all cancer patients undergo this form of treatment.
Radiation therapy has a profound impact on controlling tumor growth, reducing the risk of local recurrence, and managing cancer symptoms. Its specific effects can vary depending on several factors, including the type and stage of cancer, as well as individual patient circumstances. Despite these variations, the importance of radiation therapy in cancer treatment is indisputable.
Professionals in this field must maintain the highest standards of patient care and safety. One way they demonstrate their competence is through certification from the American Registry Of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT). This credential not only validates their proficiency but also ensures they are up-to-date with the latest advancements and best practices in radiation therapy.
ARRT certification involves a rigorous examination process, and prospective candidates often rely on tools like the radiology ARRT practice test to prepare. If you’re considering a career in this vital healthcare discipline, accessing reliable platforms for radiography practice tests should be an integral part of your preparation.
The field of radiation therapy offers a wealth of career opportunities, particularly for ARRT-certified professionals. This article aims to shed light on these prospects and the critical role ARRT certification plays in furthering a career in radiation therapy.
Radiation Therapy: An Essential Component of Cancer Treatment
Radiation Therapy: Definition and Overview
Radiation therapy is a specialized medical treatment used in managing cancer and certain non-cancerous conditions. This treatment modality involves the precise use of high-energy radiation to destroy cancer cells, shrink tumors, and alleviate symptoms. This process works by damaging the DNA within cancer cells, thereby inhibiting their ability to grow and divide.
Radiation therapy can be delivered in two primary ways. External beam radiation therapy involves a machine that directs radiation beams towards the tumor from outside the body. On the other hand, internal radiation therapy, or brachytherapy, involves placing a radioactive source near or directly into the tumor.
The choice of radiation therapy approach depends on various factors, including the type, location, and stage of cancer. A multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including radiation oncologists, radiation therapists, and medical physicists, collaborates to develop personalized treatment plans. They aim to strike a delicate balance between effectively destroying cancer cells and minimizing damage to the surrounding healthy tissues.
The Growing Demand for Professionals in Radiation Therapy
There is a significantly growing demand for professionals in radiation therapy which is due to several factors.
Firstly, there is an increasing incidence of cancer worldwide, resulting in a higher demand for radiation therapy as an integral part of cancer treatment. A study showed that 18.7 million people worldwide received a cancer diagnosis in 2010, and the total number of deaths from cancer was 8.29 million.
By 2019, there had been a substantial increase in those figures, with a staggering 23.6 million individuals being diagnosed with cancer and records indicating 10 million lives lost to the disease.
Secondly, advancements in technology and treatment techniques have expanded the scope and effectiveness of radiation therapy, further driving the need for skilled professionals.
Furthermore, the aging population contributes to the growing demand, as cancer incidence tends to increase with age. As a result, there is a pressing need for radiation therapists, dosimetrists, medical physicists, and other specialized professionals who can deliver safe and precise radiation treatments.
This growing demand underscores the importance of attracting and training individuals to meet the increasing needs of patients requiring radiation therapy services.
The Importance of ARRT Certification
ARRT certification holds immense significance for both professionals in the field of radiologic technology and their patients. This credential is a mark of excellence and proficiency, demonstrating that a professional has met the rigorous standards set by an authoritative body in the field.
For those aspiring to join this dynamic field as radiation therapists, preparation is key. This is where the role of comprehensive preparation resources comes into play. You can take your radiography practice test to better equip yourself for the ARRT certification exam, which is a necessary step to becoming a proficient professional in this field.
Standard of Excellence
Obtaining an ARRT certification signifies a practitioner’s commitment to providing the highest quality patient care. This certification process includes demonstrating competency in specific skills and knowledge areas, proving that the professional is well-equipped to handle the complexities of radiologic procedures, including radiation therapy.
Continuing Education
ARRT certification is not a one-time achievement. To maintain this certification, professionals must participate in ongoing continuing education. This requirement ensures that ARRT-certified radiologic technologists stay current with the latest developments and innovations in the field, leading to improved patient outcomes.
Patient Trust
From a patient’s perspective, seeing that their healthcare provider is ARRT-certified can provide a sense of trust and reassurance. It signifies that the professional caring for them has achieved a high standard of training and competence and is committed to adhering to a strict code of ethics.
Professional Development
ARRT certification can also open up new avenues for career advancement. Many healthcare institutions prefer or even require their staff to hold this certification, recognizing its value. Furthermore, this credential can also provide an edge in competitive job markets, signifying the professional’s dedication to the field and their ability to provide high-quality care.
In summary, ARRT certification plays a vital role in maintaining high standards in the field of radiologic technology. It signifies a professional’s proficiency, commitment to continuous learning, ethical practice, and dedication to providing the best possible patient care.
Exploring Career Paths for ARRT-Certified Professionals
Embarking on a career in radiation therapy offers a multitude of exciting possibilities for ARRT-certified professionals. This section explores career opportunities, ranging from radiation therapists, dosimetrists, and medical physicists to specialized roles in research and oncology nursing.
Radiation Therapist
A radiation therapist is a healthcare professional who plays a critical role in the delivery of radiation therapy treatments to patients with cancer or certain non-cancerous conditions.
Their primary job is to operate radiation therapy equipment, precisely administer prescribed doses of radiation, and ensure the accurate targeting of tumors while minimizing exposure to surrounding healthy tissues.
Radiation therapists require a range of essential skills to excel in their profession. These skills include:
- Technical proficiency in operating radiation therapy equipment
- Meticulous attention to detail
- Effective communication and interpersonal abilities
- Teamwork and collaboration
- Problem-solving skills
- Organization and time management,
- Compassion
- Professionalism
Additionally, continuous learning and staying updated with advancements in the field are also necessary for providing optimal patient care.
Radiation therapists can work in hospitals, cancer centers, research facilities, outpatient clinics, radiation therapy centers, and academic institutions.
However, the availability of work settings may vary depending on the location and healthcare infrastructure of a particular region.
Dosimetrist
A dosimetrist is a specialized member of the radiation therapy team who works closely with radiation oncologists and medical physicists to calculate and plan the precise radiation dosage that will be administered to patients during their treatment.
They use advanced computer software and imaging techniques to develop treatment plans that deliver the prescribed radiation dose to the tumor while minimizing exposure to healthy tissues.
Dosimetrists ensure the accuracy and safety of radiation therapy by performing calculations, conducting quality assurance checks, and collaborating with other members of the treatment team to optimize treatment plans for each patient.
Dosimetrists need a combination of technical proficiency, mathematical and analytical skills, attention to detail, problem-solving abilities, and effective communication and collaboration skills.
They typically hold a bachelor’s degree in medical dosimetry or a related field and may pursue certification through the Medical Dosimetrist Certification Board (MDCB) to demonstrate their competence and adherence to professional standards.
Medical Physicist
Medical physicists are specialized healthcare professionals who play a crucial role in radiation therapy.
Their primary responsibility is to ensure the safe and effective use of radiation in medical treatments. Medical physicists work closely with radiation oncologists and radiation therapists to develop and implement treatment plans, optimize radiation delivery techniques, and ensure quality assurance in radiation therapy procedures.
They are involved in various aspects, including radiation dose calculations, treatment planning, equipment calibration, and quality control. They also contribute to research, development, and implementation of new technologies and techniques in radiation therapy.
To become a certified medical physicist, individuals typically need to fulfill certain requirements, which may vary depending on the country or region. However, here are the general certification requirements for medical physicists:
- Education: Completion of a master’s or doctoral degree in medical physics or a related field.
- Clinical Training: Participation in a clinical training program to gain practical experience in areas such as treatment planning, radiation safety, and quality assurance.
- Residency Program: Completion of a structured residency program that provides hands-on training under the supervision of experienced medical physicists.
- Certification Examinations: Successful completion of one or more certification examinations administered by recognized certifying bodies or professional organizations.
- Continuing Education: Engagement in ongoing professional development activities to stay updated with advancements in the field and maintain certification.
Radiation Oncology Nurse
A radiation oncology nurse plays a crucial role in the care and support of patients undergoing radiation therapy for cancer treatment.
The role of a radiation oncology nurse involves assessing and caring for patients undergoing radiation therapy for cancer treatment.
They coordinate treatment plans, educate patients and their families, administer radiation therapy, and manage treatment-related side effects. They also provide emotional support, document patient information, collaborate with the healthcare team, and engage in ongoing professional development.
Their primary focus is to ensure the well-being and comfort of patients throughout their radiation therapy journey.
Oncology nurses can pursue various certifications to demonstrate their expertise in providing specialized care to patients with cancer. Common certifications include
- Oncology Certified Nurse (OCN),
- Certified Pediatric Hematology Oncology Nurse (CPHON),
- Advanced Oncology Certified Nurse Practitioner (AOCNP),
- Certified Breast Care Nurse (CBCN),
- Chemotherapy Biotherapy Certification,
- and other specialty certifications.
Oncology nurses require a diverse set of skills to provide effective care for patients with cancer. These skills include clinical competence, symptom management, effective communication, patient education, critical thinking, emotional support, teamwork and collaboration, and cultural sensitivity.
Challenges and Considerations
Starting a career in radiation therapy can present certain challenges. Some potential challenges that individuals may face include:
- Mastering complex technology
- Dealing with the emotional impact of working with cancer patients
- Ensuring radiation safety
- Adapting to patient variability
- Managing time effectively
- Collaborating with a multidisciplinary team
- Staying updated with advancements in the field
To overcome these challenges, individuals need dedication, ongoing learning, effective communication, resilience, and a patient-centered approach. With time and experience, they can successfully navigate these challenges and thrive in their radiation therapy careers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a career in radiation therapy offers promising opportunities for ARRT-certified professionals. With the increasing importance of radiation therapy in cancer treatment, there is a growing demand for skilled and qualified individuals in this field.
From radiation therapists to dosimetrists and medical physicists, each role plays a vital part in delivering effective and safe radiation treatments to patients. The required skills, qualifications, and certifications demonstrate the dedication and expertise necessary to excel in these careers.
With a commitment to ongoing learning and a passion for making a positive impact in the lives of cancer patients, individuals can embark on a rewarding journey in radiation therapy and contribute to the fight against cancer.

Aimee Garcia is a Marketing Consultant and Technical Writer at DailyTechTime. She has 5+ years of experience in Digital Marketing. She has worked with different IT companies.

